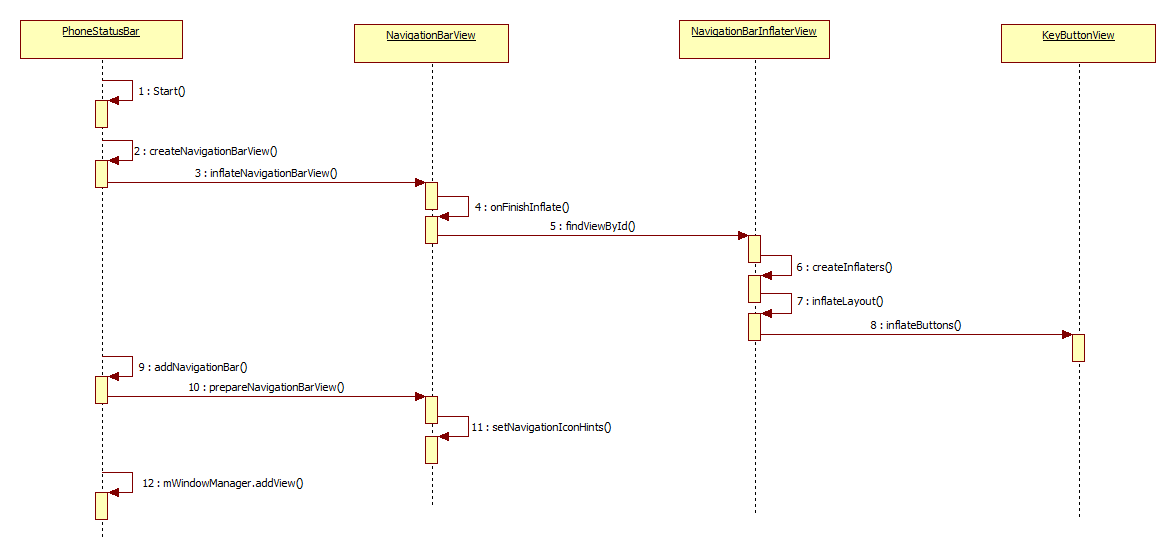
导航栏和状态栏都是通过WindowManager直接添加的View,他们一般称为装饰窗口。下面来看导航栏的创建过程。 回到之前的PhoneStatusBar中的makeStatusBarView函数中:
try {
boolean showNav = mWindowManagerService.hasNavigationBar();
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "hasNavigationBar=" + showNav);
if (showNav) {
createNavigationBarView(context);
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// no window manager? good luck with that
}
首先判断是否支持虚拟按键,判断条件逻辑在PhoneWindowManager中:
mHasNavigationBar = res.getBoolean(com.android.internal.R.bool.config_showNavigationBar);
// Allow a system property to override this. Used by the emulator.
// See also hasNavigationBar().
String navBarOverride = SystemProperties.get("qemu.hw.mainkeys");
if ("1".equals(navBarOverride)) {
mHasNavigationBar = false;
} else if ("0".equals(navBarOverride)) {
mHasNavigationBar = true;
}
决定是否显示为qemu.hw.mainkeys实体按键属性。如果支持的话,则调用createNavigationBarView创建导航栏控件树:
protected void createNavigationBarView(Context context) {
inflateNavigationBarView(context);
mNavigationBarView.setDisabledFlags(mDisabled1);
......
}
mNavigationBarView.setDisabledFlags(mDisabled1)是设置导航栏中各按键是否可见flag。 重点来看inflateNavigationBarView:
protected void inflateNavigationBarView(Context context) {
mNavigationBarView = (NavigationBarView) View.inflate(
context, R.layout.navigation_bar, null);
}
该函数加载创建了一个NavigationBarView类型的布局navigation_bar.xml:
<com.android.systemui.statusbar.phone.NavigationBarView
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:systemui="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:background="@drawable/system_bar_background">
<com.android.systemui.statusbar.phone.NavigationBarInflaterView
android:id="@+id/navigation_inflater"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</com.android.systemui.statusbar.phone.NavigationBarView>
该布局中包含一个定义布局NavigationBarInflaterView。下面重点介绍一下这两个自定义布局NavigationBarView和NavigationBarInflaterView。 首先来看NavigationBarView的创建函数:
public NavigationBarView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
.......
updateIcons(context, Confi guration.EMPTY, mConfiguration);
mBarTransitions = new NavigationBarTransitions(this);
mButtonDisatchers.put(R.id.back, new ButtonDispatcher(R.id.back));
mButtonDisatchers.put(R.id.home, new ButtonDispatcher(R.id.home));
mButtonDisatchers.put(R.id.recent_apps, new ButtonDispatcher(R.id.recent_apps));
mButtonDisatchers.put(R.id.menu, new ButtonDispatcher(R.id.menu));
mButtonDisatchers.put(R.id.ime_switcher, new ButtonDispatcher(R.id.ime_switcher));
}
updateIcons主要是初识化导航栏中各个按键的图标。 这里的初始化涉及到了ButtonDisatchers类,这个类是用于处理多个具有相同操作的虚拟按键设置。如设置图片、设置click和touch事件等。
再来看NavigationBarView的onFinishInflate函数:
public void onFinishInflate() {
mNavigationInflaterView = (NavigationBarInflaterView) findViewById(
R.id.navigation_inflater);
updateRotatedViews();
mNavigationInflaterView.setButtonDispatchers(mButtonDisatchers);
......
}
其主要创建加载了NavigationBarInflaterView布局,先来看其创建和加载函数:
public NavigationBarInflaterView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
mDensity = context.getResources().getConfiguration().densityDpi;
createInflaters();
}
创建函数中主要获取了屏幕密度和初始化布局加载器。 再看加载函数:
@Override
protected void onFinishInflate() {
super.onFinishInflate();
inflateChildren();
clearViews();
inflateLayout(getDefaultLayout());
}
首先看inflateChildren的实现:
private void inflateChildren() {
removeAllViews();
mRot0 = (FrameLayout) mLayoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.navigation_layout, this, false);
mRot0.setId(R.id.rot0);
addView(mRot0);
mRot90 = (FrameLayout) mLayoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.navigation_layout_rot90, this,
false);
mRot90.setId(R.id.rot90);
addView(mRot90);
updateAlternativeOrder();
if (getParent() instanceof NavigationBarView) {
((NavigationBarView) getParent()).updateRotatedViews();
}
}
可以看到添加了两个布局navigation_layout和navigation_layout_rot90,这两个布局分别代表水平方式和垂直方式的导航栏布局,以navigation_layout为例:
<FrameLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:systemui="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/nav_buttons"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/ends_group"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:clipChildren="false" />
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/center_group"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:clipChildren="false" />
</FrameLayout>
<com.android.systemui.statusbar.policy.DeadZone
android:id="@+id/deadzone"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="top"
systemui:minSize="@dimen/navigation_bar_deadzone_size"
systemui:maxSize="@dimen/navigation_bar_deadzone_size_max"
systemui:holdTime="@integer/navigation_bar_deadzone_hold"
systemui:decayTime="@integer/navigation_bar_deadzone_decay"
systemui:orientation="horizontal"
/>
</FrameLayout>
主要包括了nav_buttons和deadzone,nav_buttons即包含了虚拟按键子控件,子控件以ends_group和center_group布局加载,后面会详细介绍具体的子控件加载。navigation_layout_rot90和其唯一的区别在在于ends_group和center_group使用的是ReverseLinearLayout,这个布局可以自动反转子view添加的顺序,还可以反转布局参数的宽度和高度值。 deadzone是一个DeadZone类型的控件,覆盖在其他所有控件之上。这个类主要是为了避免用户误操作,其会将导航栏边缘的触摸事件当做用户误操作消费掉。
再来看updateRotatedViews的实现:
void updateRotatedViews() {
mRotatedViews[Surface.ROTATION_0] =
mRotatedViews[Surface.ROTATION_180] = findViewById(R.id.rot0);
mRotatedViews[Surface.ROTATION_270] =
mRotatedViews[Surface.ROTATION_90] = findViewById(R.id.rot90);
updateCurrentView();
}
可以看到水平方向使用的是rot0,垂直方向使用的rot90的布局,再看updateCurrentView的实现:
private void updateCurrentView() {
final int rot = mDisplay.getRotation();
for (int i=0; i<4; i++) {
mRotatedViews[i].setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
mCurrentView = mRotatedViews[rot];
mCurrentView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mNavigationInflaterView.setAlternativeOrder(rot == Surface.ROTATION_90);
for (int i = 0; i < mButtonDisatchers.size(); i++) {
mButtonDisatchers.valueAt(i).setCurrentView(mCurrentView);
}
updateLayoutTransitionsEnabled();
mCurrentRotation = rot;
}
可以看到该函数获取了当前的旋转方向,然后选择相应的布局显示。
然后回到onFinishInflate,初始化好相应布局后,调用clearViews清除布局的相应子view,然后调用inflateLayout设置布局的相关控件,来看其实现:
protected void inflateLayout(String newLayout) {
mCurrentLayout = newLayout;
if (newLayout == null) {
newLayout = getDefaultLayout();
}
String[] sets = newLayout.split(GRAVITY_SEPARATOR, 3);
String[] start = sets[0].split(BUTTON_SEPARATOR);
String[] center = sets[1].split(BUTTON_SEPARATOR);
String[] end = sets[2].split(BUTTON_SEPARATOR);
// Inflate these in start to end order or accessibility traversal will be messed up.
inflateButtons(start, (ViewGroup) mRot0.findViewById(R.id.ends_group), false);
inflateButtons(start, (ViewGroup) mRot90.findViewById(R.id.ends_group), true);
inflateButtons(center, (ViewGroup) mRot0.findViewById(R.id.center_group), false);
inflateButtons(center, (ViewGroup) mRot90.findViewById(R.id.center_group), true);
addGravitySpacer((LinearLayout) mRot0.findViewById(R.id.ends_group));
addGravitySpacer((LinearLayout) mRot90.findViewById(R.id.ends_group));
inflateButtons(end, (ViewGroup) mRot0.findViewById(R.id.ends_group), false);
inflateButtons(end, (ViewGroup) mRot90.findViewById(R.id.ends_group), true);
}
getDefaultLayout是获取一串定义的字符串:
<string name="config_navBarLayout" translatable="false">space,back;home;recent,menu_ime</string>
然后解析这一个字串并保存,这个字串其实就是设置三个虚拟按键可以显示的内容。其是通过inflateButton函数来实现的。来看实现:
protected View inflateButton(String buttonSpec, ViewGroup parent, boolean landscape,
int indexInParent) {
LayoutInflater inflater = landscape ? mLandscapeInflater : mLayoutInflater;
float size = extractSize(buttonSpec);
String button = extractButton(buttonSpec);
View v = null;
if (HOME.equals(button)) {
v = inflater.inflate(R.layout.home, parent, false);
if (landscape && isSw600Dp()) {
setupLandButton(v);
}
} else if (BACK.equals(button)) {
v = inflater.inflate(R.layout.back, parent, false);
if (landscape && isSw600Dp()) {
setupLandButton(v);
}
} else if (RECENT.equals(button)) {
v = inflater.inflate(R.layout.recent_apps, parent, false);
if (landscape && isSw600Dp()) {
setupLandButton(v);
}
} else if (MENU_IME.equals(button)) {
v = inflater.inflate(R.layout.menu_ime, parent, false);
} else if (NAVSPACE.equals(button)) {
v = inflater.inflate(R.layout.nav_key_space, parent, false);
} else if (CLIPBOARD.equals(button)) {
v = inflater.inflate(R.layout.clipboard, parent, false);
} else if (button.startsWith(KEY)) {
String uri = extractImage(button);
int code = extractKeycode(button);
v = inflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_key, parent, false);
((KeyButtonView) v).setCode(code);
if (uri != null) {
((KeyButtonView) v).loadAsync(uri);
}
} else {
return null;
}
if (size != 0) {
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = v.getLayoutParams();
params.width = (int) (params.width * size);
}
parent.addView(v);
addToDispatchers(v, landscape);
View lastView = landscape ? mLastRot90 : mLastRot0;
if (lastView != null) {
v.setAccessibilityTraversalAfter(lastView.getId());
}
if (landscape) {
mLastRot90 = v;
} else {
mLastRot0 = v;
}
return v;
}
可以看到根据相应的String设置不同的布局文件,以home为例,其加载的为home layout:
<com.android.systemui.statusbar.policy.KeyButtonView
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:systemui="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:id="@+id/home"
android:layout_width="@dimen/navigation_key_width"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="0"
android:src="@drawable/ic_sysbar_home"
systemui:keyCode="3"
android:scaleType="center"
android:contentDescription="@string/accessibility_home"
android:paddingStart="@dimen/navigation_key_padding"
android:paddingEnd="@dimen/navigation_key_padding"
/>
其是一个KeyButtonView类型的子控件,KeyButtonView继承自ImageView,主要扩展的功能是根据派发给它的触摸事件转化为按键事件,并通过InputManager.injectInputEvent方法将按键事件注入到InputDispatcher的派发队列中,模拟按键输入。 在KeyButtonView中比较重要的字段为mCode和mSupportsLongpress,表示按键事件的键值和是否产生按键的长按事件,这两个值的定义是通过自定义控件的属性keyCode和keyRepeat设置的,但是长按事件在这里都没有设置,长按事件的处理都是通过设置相关监听事件,后面会介绍。如下为代码分析:
<declare-styleable name="KeyButtonView">
<!-- key code to send when pressed; if absent or 0, no key is sent -->
<attr name="keyCode" format="integer" />
<!-- does this button generate longpress / repeat events? -->
<attr name="keyRepeat" format="boolean" />
<attr name="android:contentDescription" />
</declare-styleable>
这是属性的定义,在上面的 systemui:keyCode=”3”即为设置Home的键值。下面来看KeyButtonView中的处理,首先是初始化:
public KeyButtonView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.KeyButtonView,
defStyle, 0);
mCode = a.getInteger(R.styleable.KeyButtonView_keyCode, 0);
mSupportsLongpress = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.KeyButtonView_keyRepeat, true);
......
setClickable(true);
......
setBackground(new KeyButtonRipple(context, this));
}
可以看到,首先获取定义的键值和是否支持长按,并设置为可点击和背景。下面看OnTouch事件处理:
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
......
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
setPressed(true);
......
if (mCode != 0) {
sendEvent(KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN, 0, mDownTime);
}
......
postDelayed(mCheckLongPress, ViewConfiguration.getLongPressTimeout());
......
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
setPressed(false);
if (mCode != 0) {
sendEvent(KeyEvent.ACTION_UP, KeyEvent.FLAG_CANCELED);
}
removeCallbacks(mCheckLongPress);
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
final boolean doIt = isPressed() && !mLongClicked;
setPressed(false);
if (mCode != 0) {
if (doIt) {
sendEvent(KeyEvent.ACTION_UP, 0);
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED);
} else {
sendEvent(KeyEvent.ACTION_UP, KeyEvent.FLAG_CANCELED);
}
} else {
// no key code, just a regular ImageView
if (doIt && mOnClickListener != null) {
mOnClickListener.onClick(this);
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED);
}
}
removeCallbacks(mCheckLongPress);
break;
}
return true;
}
private final Runnable mCheckLongPress = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
if (isPressed()) {
// Log.d("KeyButtonView", "longpressed: " + this);
if (isLongClickable()) {
// Just an old-fashioned ImageView
performLongClick();
mLongClicked = true;
} else if (mSupportsLongpress) {
sendEvent(KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN, KeyEvent.FLAG_LONG_PRESS);
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_LONG_CLICKED);
mLongClicked = true;
}
}
}
};
可以看到,不管是按键还是长按事件,最终都会调用sendEvent发送相应的事件,下面来看其实现:
void sendEvent(int action, int flags, long when) {
final int repeatCount = (flags & KeyEvent.FLAG_LONG_PRESS) != 0 ? 1 : 0;
final KeyEvent ev = new KeyEvent(mDownTime, when, action, mCode, repeatCount,
0, KeyCharacterMap.VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD, 0,
flags | KeyEvent.FLAG_FROM_SYSTEM | KeyEvent.FLAG_VIRTUAL_HARD_KEY,
InputDevice.SOURCE_KEYBOARD);
InputManager.getInstance().injectInputEvent(ev,
InputManager.INJECT_INPUT_EVENT_MODE_ASYNC);
}
可以看到最后是通过InputManager.injectInputEvent将keyEvent加入到InputDispatcher的派发队列,模式按键的输入事件。 总结一下: 如设置了keyCode,则通过OnTouchEvent完成从触摸事件到按键事件的映射,在通过SendEvent完成按键事件的创建与发送。 如没有设置KeyCode,则触发监听器OnClickListener,执行对应的处理函数。
到这里,布局的创建基本已经完成,但是具体的按键图标还未设置,前面的NavigationBarView的初始化中,updateIcons只是获取了相关的图标资源,并未设置到具体的控件中,下面就接着来看。 回到PhoneStatusBar的Start函数中,在执行完super.start()后,紧着着执行的是addNavigationBar()函数,我们来看其实现:
protected void addNavigationBar() {
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "addNavigationBar: about to add " + mNavigationBarView);
if (mNavigationBarView == null) return;
try {
WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowManagerService()
.watchRotation(new IRotationWatcher.Stub() {
@Override
public void onRotationChanged(final int rotation) throws RemoteException {
// We need this to be scheduled as early as possible to beat the redrawing of
// window in response to the orientation change.
Message msg = Message.obtain(mHandler, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mNavigationBarView != null
&& mNavigationBarView.needsReorient(rotation)) {
repositionNavigationBar();
}
}
});
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
mHandler.sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue(msg);
}
});
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
prepareNavigationBarView();
mWindowManager.addView(mNavigationBarView, getNavigationBarLayoutParams());
首先注册了一个方向变化的监听,用于在变化时及时更新。 下面的prepareNavigationBarView和mWindowManager.addView是初始化的重点函数。 先来看prepareNavigationBarView:
private void prepareNavigationBarView() {
mNavigationBarView.reorient();
ButtonDispatcher recentsButton = mNavigationBarView.getRecentsButton();
recentsButton.setOnClickListener(mRecentsClickListener);
recentsButton.setOnTouchListener(mRecentsPreloadOnTouchListener);
recentsButton.setLongClickable(true);
recentsButton.setOnLongClickListener(mRecentsLongClickListener);
ButtonDispatcher backButton = mNavigationBarView.getBackButton();
backButton.setLongClickable(true);
backButton.setOnLongClickListener(mLongPressBackListener);
ButtonDispatcher homeButton = mNavigationBarView.getHomeButton();
homeButton.setOnTouchListener(mHomeActionListener);
homeButton.setOnLongClickListener(mLongPressHomeListener);
mAssistManager.onConfigurationChanged();
}
看NavigationBarView中reorient的实现:
public void reorient() {
updateCurrentView();
getImeSwitchButton().setOnClickListener(mImeSwitcherClickListener);
mDeadZone = (DeadZone) mCurrentView.findViewById(R.id.deadzone);
// force the low profile & disabled states into compliance
mBarTransitions.init();
setDisabledFlags(mDisabledFlags, true /* force */);
setMenuVisibility(mShowMenu, true /* force */);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "reorient(): rot=" + mCurrentRotation);
}
updateTaskSwitchHelper();
setNavigationIconHints(mNavigationIconHints, true);
}
主要是更新水平or垂直布局,并设置是否弹出输入法的相关显示即监听事件,最后是setNavigationIconHints函数,我们来看这里面的实现:
public void setNavigationIconHints(int hints, boolean force) {
if (!force && hints == mNavigationIconHints) return;
final boolean backAlt = (hints & StatusBarManager.NAVIGATION_HINT_BACK_ALT) != 0;
if ((mNavigationIconHints & StatusBarManager.NAVIGATION_HINT_BACK_ALT) != 0 && !backAlt) {
mTransitionListener.onBackAltCleared();
}
if (DEBUG) {
android.widget.Toast.makeText(getContext(),
"Navigation icon hints = " + hints,
500).show();
}
mNavigationIconHints = hints;
// We have to replace or restore the back and home button icons when exiting or entering
// carmode, respectively. Recents are not available in CarMode in nav bar so change
// to recent icon is not required.
Drawable backIcon = (backAlt)
? getBackIconWithAlt(mUseCarModeUi, mVertical)
: getBackIcon(mUseCarModeUi, mVertical);
getBackButton().setImageDrawable(backIcon);
updateRecentsIcon();
if (mUseCarModeUi) {
getHomeButton().setImageDrawable(mHomeCarModeIcon);
} else {
getHomeButton().setImageDrawable(mHomeDefaultIcon);
}
final boolean showImeButton = ((hints & StatusBarManager.NAVIGATION_HINT_IME_SHOWN) != 0);
getImeSwitchButton().setVisibility(showImeButton ? View.VISIBLE : View.INVISIBLE);
getImeSwitchButton().setImageDrawable(mImeIcon);
// Update menu button in case the IME state has changed.
setMenuVisibility(mShowMenu, true);
getMenuButton().setImageDrawable(mMenuIcon);
setDisabledFlags(mDisabledFlags, true);
可以看到这个函数就是将具体的图标资源设置到相关的控件中。
回到前面prepareNavigationBarView中,执行完reorient后,获取了相关的button并设置了相关按键事件的监听,包括点击和长按。前面提到,对于设置了KeyCode的keyButtonView(home、back),则在KeyButtonView中会解析并发送相应的按键事件,而对于未设置的(recent),则是在这里设置相应的click事件。对于长按事件,三个按键都是在这里设置。
在回到addNavigationBar中,执行完prepareNavigationBarView后,则控件树和资源都基本已加载完,就剩最后一步,将控件树加载到Window中,即mWindowManager.addView,其中相关的添加参数在getNavigationBarLayoutParams中:
private WindowManager.LayoutParams getNavigationBarLayoutParams() {
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = new WindowManager.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_NAVIGATION_BAR,
0
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_TOUCHABLE_WHEN_WAKING
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SPLIT_TOUCH
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SLIPPERY,
PixelFormat.TRANSLUCENT);
// this will allow the navbar to run in an overlay on devices that support this
if (ActivityManager.isHighEndGfx()) {
lp.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED;
}
lp.setTitle("NavigationBar");
lp.windowAnimations = 0;
return lp;
}
至此,导航栏就已经添加创建完毕。
下面总结一下导航栏的控件树及其加载过程。
整体控件树如下:
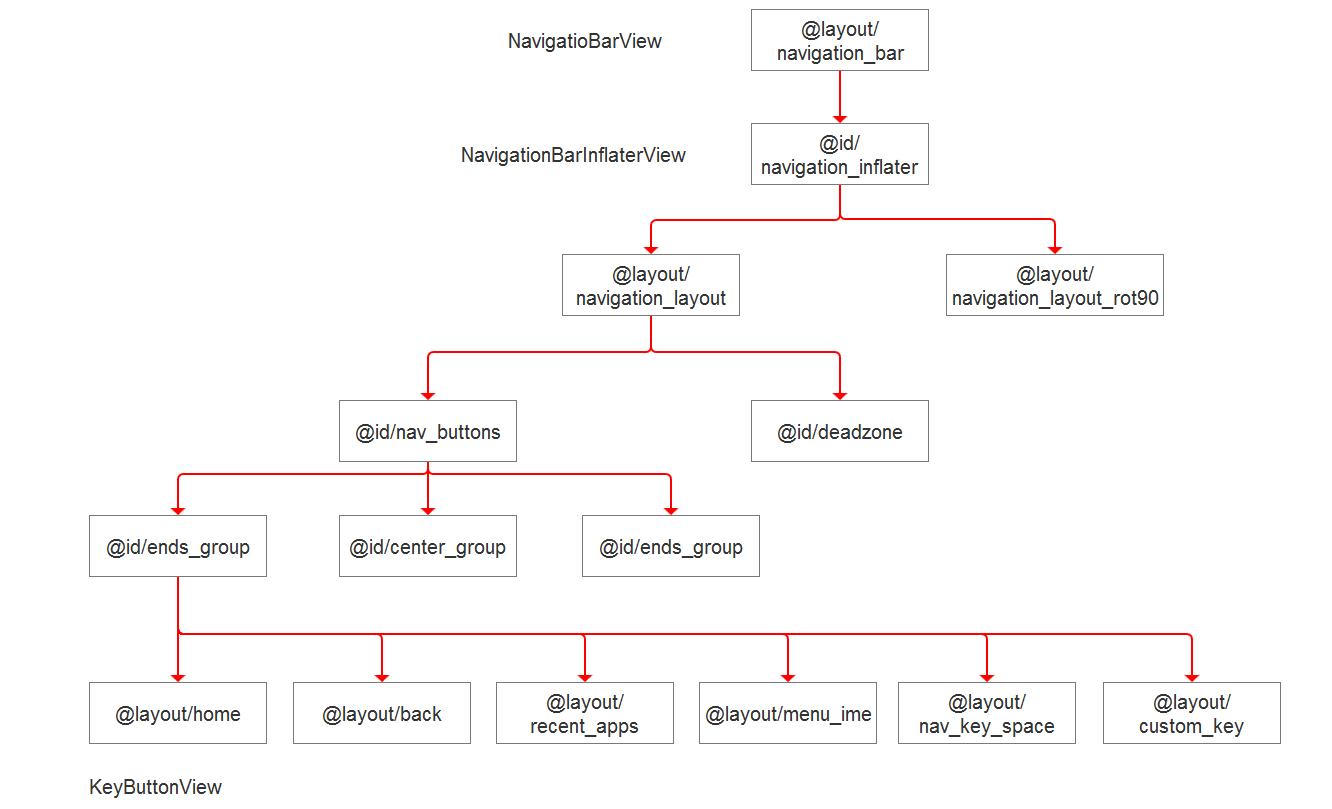
加载过程如下: